1. 서론
지난 포스팅에서 Command Application에 대한 전반적인 구현을 마무리했습니다. 하지만 해당 프로그램은 근본적인 문제점을 안고 있습니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 발생되는 문제점과 이를 해결하기 위한 방법에 대하여 살펴보겠습니다.
2. 문제점 도출
아래 테이블은 계정 생성 Command를 실행했을 때 EventStore에 저장되는 데이터 중 일부를 발췌한 것입니다.
| 글로벌 인덱스 | Payload |
Payload 종류 |
발생 시간 | Aggregate 식별자 | 시퀀스 번호 | 타입 |
| 1 | com.cqrs.events.HolderCreationEvent | 2019-12-29T05:34:49.2527378Z | 70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e | 0 | HolderAggregate |
공간 부족으로 위 데이터에서 Payload 데이터만 따로 뽑아보면 다음과 같습니다.
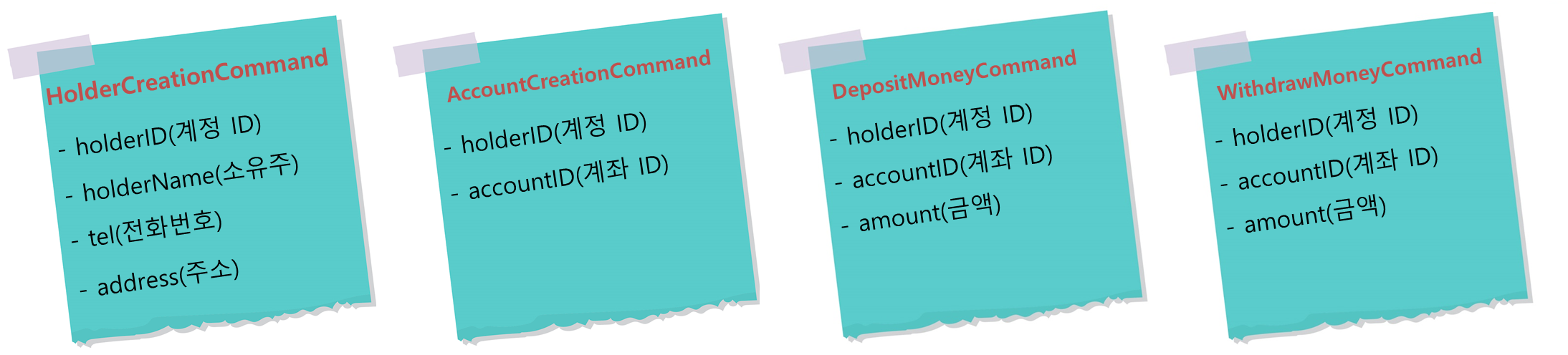
<com.cqrs.events.HolderCreationEvent>
<holderID>70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e</holderID>
<holderName>kevin</holderName>
<tel>02-1234-5678</tel>
<address>OO시 OO구/address>
</com.cqrs.events.HolderCreationEvent>Payload에는 Event 내용이 담겨있습니다. 따라서 EventSourcing 및 Event Handler에서는 Payload 내용을 기준으로 Event를 처리합니다.
계정 생성만 완료된 상황에서 추가로 계좌 생성 > 계좌 입금(300원) > 인출 5회(1원씩)을 진행한 후 EventStore를 살펴보면 다음과 같습니다.
| 글로벌 인덱스 |
Payload 종류 |
Aggregate 식별자 | 시퀀스 번호 | 타입 |
| 1 | com.cqrs.events.HolderCreationEvent | 70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e | 0 | HolderAggregate |
| 2 | com.cqrs.events.AccountCreationEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 0 | AccountAggregate |
| 3 | com.cqrs.events.DepositMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 1 | AccountAggregate |
| 4 | com.cqrs.events.WithdrawMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 2 | AccountAggregate |
| 5 | com.cqrs.events.WithdrawMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 3 | AccountAggregate |
| 6 | com.cqrs.events.WithdrawMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 4 | AccountAggregate |
| 7 | com.cqrs.events.WithdrawMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 5 | AccountAggregate |
| 8 | com.cqrs.events.WithdrawMoneyEvent | c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 6 | AccountAggregate |
(※ 공간 부족으로 Payload 및 이벤트 발생 시간 등은 제외하였습니다.)
만약 이러한 상황에서 c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 식별자를 지닌 AccountAggregate 에서 1원을 인출하는 명령이 발생된다면 내부적으로는 어떠한 과정을 거칠까요?

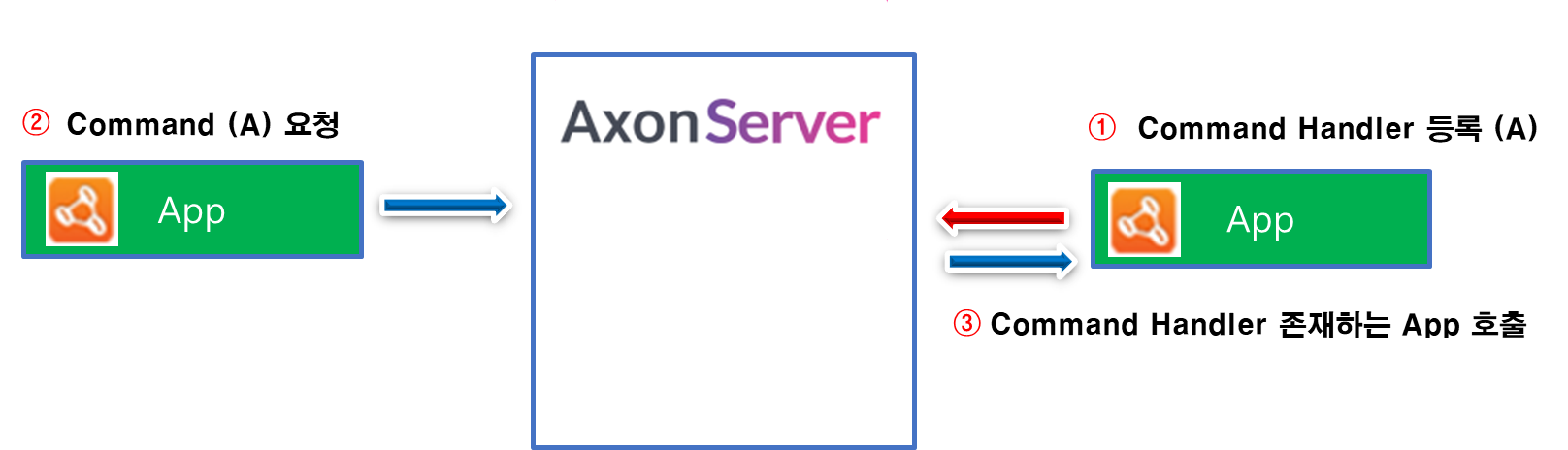
Command 어플리케이션 구현 - 1 포스팅에서 소개한 Command 이벤트 수행 내부 흐름도입니다. 당시 4번 과정에 대해서 다음과 같이 소개했습니다.
| 4. UnitOfWork 수행합니다. 이 과정에서 Chain으로 연결된 handler 들을 거치면서 대상 Aggregate에 대하여 EventStore로부터 과거 이벤트들을 Loading 하여 최신 상태로 만듭니다. 이후 해당 Command와 연결된 Handler 메소드를 Reflection을 활용하여 호출합니다. |
즉 새로운 명령을 수행하기 위해서는 c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 식별자를 지닌 Aggregate를 대상으로 기존에 발행된 7개의 이벤트를 EventStore에서 읽어와 Loading하는 작업이 선행됩니다. 그 결과 최신 상태로 Aggregate를 만든 이후에 새 Command 적용 및 Event를 발생시킵니다.
o.a.commandhandling.SimpleCommandBus : Handling command [com.cqrs.command.commands.WithdrawMoneyCommand]
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying AccountCreationEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying DepositMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=300)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 300
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 299
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 298
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 297
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 296
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 295
org.axonframework.messaging.Scope : Clearing out ThreadLocal current Scope, as no Scopes are present
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : handling WithdrawMoneyCommand(accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 294
위 코드는 Application에서 수행된 로그 중 일부를 발췌한 내용입니다.
이를 통해 알 수 있는 사실은 동일 Aggregate에 대해서 Event 갯수가 늘어날 수록 새로운 Command를 적용하는데 오랜 시간이 소요된다는 점입니다.
3. 개선 방안(Snapshot)
EventSourcing 패턴을 적용하는 Application에는 이전 단계에서 확인한 근본적인 문제점을 안고 있습니다. 따라서 이를 완화하기 위해서 일정 주기별로 Aggregate에 대한 Snapshot을 생성해야합니다.

Snapshot이란 특정 시점의 Aggregate의 상태를 말합니다. 일반적으로 EventStore에는 Aggregate의 상태를 저장하지 않고 이벤트만 저장합니다. 하지만 특정 시점의 Aggregate의 상태를 저장하여 Loading 과정에서 Snapshot 이후 Event만 Replay하여 빠르게 Aggregate Loading이 가능합니다.
AxonFramework에서도 Configuration 설정을 통해서 Aggregate 별로 Snapshot 설정이 가능합니다. Snapshot 설정에는 특정 Threshold를 넘어가면 생성되며, Snapshot 적용 예제를 통해 문제점을 완화해보도록 하겠습니다.
1. Command 모듈 AxonConfig 파일을 오픈합니다.

2. AxonConfig 클래스에 내용을 추가합니다.
AxonConfig.java
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(AxonAutoConfiguration.class)
public class AxonConfig {
@Bean
SimpleCommandBus commandBus(TransactionManager transactionManager){
return SimpleCommandBus.builder().transactionManager(transactionManager).build();
}
@Bean
public AggregateFactory<AccountAggregate> aggregateFactory(){
return new GenericAggregateFactory<>(AccountAggregate.class);
}
@Bean
public Snapshotter snapshotter(EventStore eventStore, TransactionManager transactionManager){
return AggregateSnapshotter
.builder()
.eventStore(eventStore)
.aggregateFactories(aggregateFactory())
.transactionManager(transactionManager)
.build();
}
@Bean
public SnapshotTriggerDefinition snapshotTriggerDefinition(EventStore eventStore, TransactionManager transactionManager){
final int SNAPSHOT_TRHRESHOLD = 5;
return new EventCountSnapshotTriggerDefinition(snapshotter(eventStore,transactionManager),SNAPSHOT_TRHRESHOLD);
}
@Bean
public Repository<AccountAggregate> accountAggregateRepository(EventStore eventStore, SnapshotTriggerDefinition snapshotTriggerDefinition){
return EventSourcingRepository
.builder(AccountAggregate.class)
.eventStore(eventStore)
.snapshotTriggerDefinition(snapshotTriggerDefinition)
.build();
}
}
위 코드는 AccountAggregate 기준으로 Snapshot을 설정하도록 작성된 코드입니다. SnapshotTriggerDefinition을 통하여 Aggregate의 발행된 Event가 5개 이상일 경우 Snapshot을 생성하도록 지정하였습니다. Threshold 값에는 얼마를 지정 해야한다는 기준은 없으며, 비즈니스 로직에 따라 생성 주기를 조절하면 됩니다.
Snapshot 설정을 완료한 다음 Application을 재시작 한다음 다시 API 테스트를 하면 수행 당시에는 Snapshot이 존재하지 않기 때문에 전체를 Loading 합니다. 이때 Event를 적용하는 과정에서 Threshold 값을 넘었기 때문에 EventStore에 Snapshot을 새롭게 생성합니다.
| Aggregate 식별자 | 시퀀스 번호 |
타입 |
Payload | Payload 타입 |
| c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203 | 8 | AccountAggregate | com.cqrs.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate |
생성된 Snapshot 데이터 중 일부를 발췌했습니다. 특정 시퀀스 번호에 해당되는 Aggregate에 대한 상태 정보가 기입되었으며, 상태정보는 Payload에 담겨있습니다.
Payload 내용
<com.cqrs.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate>
<accountID>c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203</accountID>
<holderID>70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e</holderID>
<balance>293</balance>
</com.cqrs.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate>
Snapshot 생성 이후 다시 1원을 인출하게되면, 이전 시퀀스 번호인 8번 Snaphot이 존재하므로 전체 Event를 읽어오지 않고 Snapshot정보를 읽어온 다음 Command 명령을 수행합니다.
o.a.commandhandling.SimpleCommandBus : Handling command [com.cqrs.command.commands.WithdrawMoneyCommand]
org.axonframework.messaging.Scope : Clearing out ThreadLocal current Scope, as no Scopes are present
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : handling WithdrawMoneyCommand(accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : applying WithdrawMoneyEvent(holderID=70f956e3-069c-4666-b0f4-324dfb0a807e, accountID=c65f80c3-9c44-4ca6-a977-72983a675203, amount=1)
c.c.command.aggregate.AccountAggregate : balance 292
org.axonframework.messaging.Scope : Clearing out ThreadLocal current Scope, as no Scopes are present
Snapshot 생성 이후 5번의 Event 발생까지는 Snapshot 시점 이전부터 생성된 Event가 재생됩니다. 만약 다시 Threshold를 넘어서게 되면 새로운 Snapshot이 생성되고 그 이후부터는 새로운 Snapshot 이후 Event가 재생됩니다.
4. 성능개선
Aggregate를 매번 로딩하면 이를 복원하는데 드는 비용이 지속 수반됩니다. 따라서 자주 사용하는 Aggregate는 Cache를 적용하면 Loading 비용이 줄어들 것입니다. Axon에서 이를 위해 기본적으로 WeakReferenceCache를 제공하며 이를 적용한 Configuration은 다음과 같습니다.
AxonConfig.java
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(AxonAutoConfiguration.class)
public class AxonConfig {
@Bean
public AggregateFactory<AccountAggregate> aggregateFactory(){
return new GenericAggregateFactory<>(AccountAggregate.class);
}
@Bean
public Snapshotter snapshotter(EventStore eventStore, TransactionManager transactionManager){
return AggregateSnapshotter
.builder()
.eventStore(eventStore)
.aggregateFactories(aggregateFactory())
.transactionManager(transactionManager)
.build();
}
@Bean
public SnapshotTriggerDefinition snapshotTriggerDefinition(EventStore eventStore, TransactionManager transactionManager){
final int SNAPSHOT_TRHRESHOLD = 5;
return new EventCountSnapshotTriggerDefinition(snapshotter(eventStore,transactionManager),SNAPSHOT_TRHRESHOLD);
}
@Bean
public Cache cache(){
return new WeakReferenceCache();
}
@Bean
public Repository<AccountAggregate> accountAggregateRepository(EventStore eventStore, SnapshotTriggerDefinition snapshotTriggerDefinition, Cache cache){
return CachingEventSourcingRepository
.builder(AccountAggregate.class)
.eventStore(eventStore)
.snapshotTriggerDefinition(snapshotTriggerDefinition)
.cache(cache)
.build();
}
}5. 마치며
3개의 포스팅을 통해 Command Application을 구현하는 방법에 대해서 살펴보았습니다. 다음 포스팅은 Aggregate 관련 번외편을 진행할 예정입니다. 따라서 데모 프로젝트를 위한 Application 구현은 이번 포스팅이 마지막입니다.
'MSA > AxonFramework' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 10. EventStore (0) | 2020.01.02 |
|---|---|
| 9. Command 어플리케이션 구현 - 4 (0) | 2019.12.31 |
| 7. Command 어플리케이션 구현 - 2 (2) | 2019.12.28 |
| 6. Command 어플리케이션 구현 - 1 (1) | 2019.12.27 |
| 5. Axon Framework 기본 구성 및 Axon Server 연동 (3) | 2019.12.26 |